

So, here we will be mocking the AWS DynamoDB with the help of the Moto Python module. Running a DynamoDB instance locally is great for testing or just messing around without incurring any cost - it's works exactly the same as the DynamoDB in the cloud All you need to do is to create a local instance and add an endpoint (JS), or endpointurl (Python) option pointing to it when creating a DynamoDB object in the AWS SDK, or a -endpoint-url option when using the CLI. In the given function, it uses DynamoDB resources to store the data. Here is a test dockerfile that will reproduce the error: FROM python:3. This is the simplest method that we can take to illustrate the working of mocking AWS DynamoDB. (self.host, self.port), self.timeout, **extra_kw)įile "/usr/local/lib/python3.4/site-packages/botocore/vendored/requests/packages/urllib3/util/connection.py", line 88, in create_connectionįile "/usr/local/lib/python3.4/site-packages/botocore/vendored/requests/packages/urllib3/util/connection.py", line 78, in create_connectionĬonnectionRefusedError: Connection refusedī.ConnectionError: ('Connection aborted.', ConnectionRefusedError(111, 'Connection refused'))
#Connect to local dynamodb python code#
Running the same code from inside the container shell: python dyn.pyįile "/usr/local/lib/python3.4/site-packages/botocore/vendored/requests/packages/urllib3/connection.py", line 155, in connectįile "/usr/local/lib/python3.4/site-packages/botocore/vendored/requests/packages/urllib3/connection.py", line 134, in _new_conn Running this from the host, here is my output: (workbench) python dyn.pyĬreated table: dynamodb.Table(name='foo') Here is some test code that reproduces the error: import boto3Įndpoint_url=' region_name='dummy_region',Īws_secret_access_key='dummy_secret_key', All you need to do, is to tell the DynamoDB or DocumentClient to use the local endpoint in the. The database will be ran with following parameters: Port: 62224 Region: us-fake-1 AWS Access Key ID: fake Connecting to DynamoDB Local using SDK. I does not help to link my ~/.aws directory as a volume. Under the hood, it will simply spin a Java process with a copy of Java-based local DynamoDB. One guess is that there are some environment variables missing, but I can't figure it out. I've tried running DynamoDB local in a container and linking it to the app's docker container, and running it on the host. However, I get a "connection refused error" when hitting it from a docker container. In this tutorial, you use the AWS SDK for Python (Boto3) to write simple programs to perform the following Amazon DynamoDB operations: Create a table called Movies and load sample data in JSON format. I can access DynamoDB local from the host without problems. I found a Docker compose file which sets up the network and container in rynop's answer on StackOverflow.For testing, I am trying to run my python 3.4 application from inside docker, and connect to a DynamoDB Local instance. The process for this varies slightly depending on how you're testing your code though and what you're making.Īt the time I was first trying to do this, I was building a serverless API with AWS SAM using AWS SAM local for testing, which would do a complete API Gateway in a container so I needed the SAM container and the DynamoDB container to talk to each other over the network. The easiest method is via the DynamoDB Docker image.
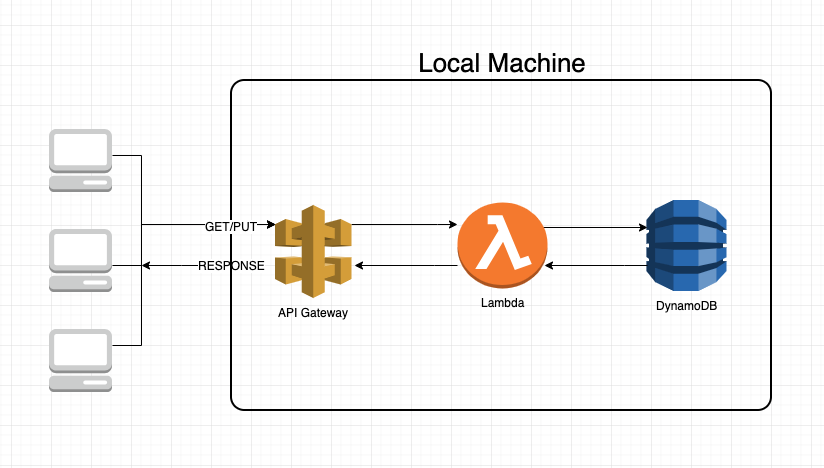
Running a DynamoDB instance locally is great for testing or just messing around without incurring any cost - it's works exactly the same as the DynamoDB in the cloud All you need to do is to create a local instance and add an endpoint (JS), or endpoint_url (Python) option pointing to it when creating a DynamoDB object in the AWS SDK, or a -endpoint-url option when using the CLI.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
